ChipXR
Transforming Semiconductor Education
with Immersive XR Training

Overview
As the lead UX researcher and designer, I end-to-end designed a mixed reality learning tool, collaborating cross-functionally throughout the process. Through multiple rounds of user testing, I played a key role in shaping the design direction and demonstrating its educational impact.
Role
UX Researcher
UX Designer
Team
1 HCI Researcher
1 Project Manager
1 UX Designer
2 Software Engineers
2 Technical Artists
2 Content Experts
Timeline
Dec 2024 - May 2025
Publication
Problem
The current education lacks
resources for engineering students
to understand complex semiconductor chips


Problem 1
3D chip structures are hard to understand with traditional flat materials

Problem 2
Hands-on laboratory experience is limited
due to expensive cost and feasibility
Solution
Leverage mixed reality (MR)
to overcome the constraints
01 Learn
Explore chip components and its structure
with interactive 3D models

Visualize complex structures in 3D
and get hands-on experience virtually
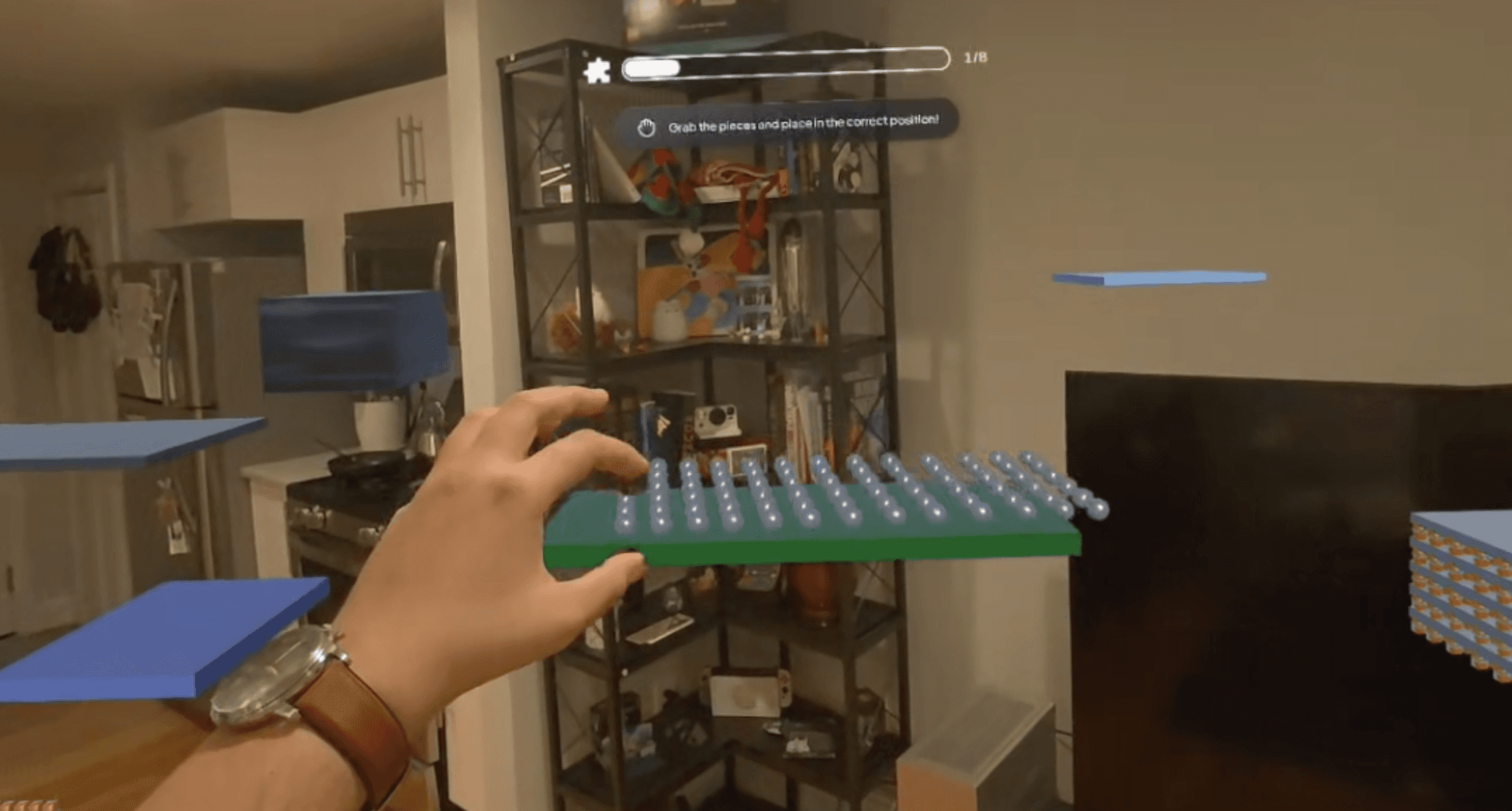
02 Assemble
Reinforce visual-spatial understanding through LEGO-like quizzes

03 Fabricate
Perform hands-on fabrication tasks to build the chip

Research
Round 1 User Testing
Concept Test
Since MR is an emerging technology, there was limited guidance to inform the design. So I tested an MVP to inform design direction and identify potential risks.
Goal
Identify potential usability risks
Method
Observation
Participants
12 Engineering students


And I discovered..
Inefficient design creates
wrong cognitive load, which can
negatively impact learning
Usability Issue
Virtual objects blended into the physical background, causing users visual confusion that led to interaction errors.
🤯
Cognitive overload!
What's happening inside their brain..
Our brain capacity is limited.
We don't want to waste our brain power like this..
extraneous load
unnecessary cognitive load
from interaction failure :(
This looks right.
germane load
good cognitive load used for actual learning! :)
Design Principle
How might we design
MR learning experience to
minimize cognitive overload?
Design Intervention
Strategy 1.
Add visual clarity
through signifiers
Signaling Principle
Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning
After
Various visual cues were used to minimize the cognitive load associated with interaction and interface, helping users stay focused on learning.
Before
Virtual objects are scattered throughout the space
Interactive spatial marker
Designate object locations and indicate their status clearly
Highlights
Signify to users what is interactable
Guiding hands
Reduce confusion by directing user attention




Strategy 2.
Chunk into
digestible pieces
Segmenting Principle
Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning
A long lesson was broken into smaller modules with manageable learning tasks.
Modular Lessons
STEP 1
Learn
Goal
Identify key components and their functions in chip structure
User Task
Interact with 3D chip component models with accompanying audio explanations
STEP 2
Assemble
Goal
Reinforce comprehension of the components and their relationships in the overall structure
User Task
Place component pieces in correct order to build complete structure
STEP 3
Fabricate
Goal
Understand the chip fabrication process by linking structural elements to procedural flows
User Task
Perform hands-on fabrication tasks to build the chip
Step-by-step breakdown of fabrication process
Fabrication Process
Photolithography
01
Etching
02
Electrodeposition
03
Wafer Bumping
04
Compute Die -
Base Die Attach
05
TSV Reveal
06
Electrodeposition
07
Solder Reflow
08
PCB Attach
09
Test
Round 2 User Testing
Evaluation
Goal
Evaluate learning effectiveness and usability
Method
Think-aloud session
Focus group
Focus group
Pre-post test
Thematic analysis
Participants
9 Engineering students from semiconductor advanced packaging course
Procedure
3 user testings were conducted with 3 participants per session.
1
Pre-test
Subjective knowledge
Objective knowledge
2
Think-aloud session
Users wear VR headset and engage with the app
3
Post-test
Subjective knowledge
Objective knowledge
4
Focus group
Qualitative assessment
Impact
ChipXR enhanced
spatial understanding with visualization
and confidence through safe, hands-on practice
Learning Progress
Quiz Score
(Objective Knowledge)
+17.6
%
Perceived Knowledge
(Subjective Knowledge)
+31.7
%
Usability
Target Completion Time
< 20
min
Success Rate
100
%
Quotes from focus groups
"Seeing the assembly visually helped a lot"
“Especially in fabrication—mistakes are expensive.
That’s why VR is great.
You can fail without breaking anything”
“Getting that hands-on experience really helped
solidify what I had only understood
in a vague way before”
More projects?

*
*